All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents

Communicate these concerns to pertinent task groups, follow up until there's an option, and report the client resolution. Make sure that all jobs are following their budgets and shipment times. Make a habit of tracking job turning points and dependences. Include these things in your routine records. Work together with other pertinent divisions, including the product, sales, and assistance divisions.
Create a system to plan, track, and file every solitary program you take care of. At the very least 4-6 years of experience in program monitoring with IT projects is critical.
Development is nitty-gritty when it pertains to the modern technology market, and within that paradigm, there's a behind-the-scenes orchestrator making sure everything runs seamlesslythe Technical Program Manager (TPM). This unhonored hero plays a crucial duty in the success of technology tasks, bringing order to turmoil and ensuring that the gears of development turn smoothly.
How does a Amazon Tpm Interview Process differ from a project manager?
It's a delicate dance in between establishing enthusiastic goals and guaranteeing expectations remain firmly grounded actually - technical project manager interview questions. technical program manager google. However it's not nearly developing a plan; it has to do with executing it flawlessly. TPMs use the hats of both visionary coordinators and practical administrators, making certain that every action straightens with the overarching task objectives

In the substantial landscape of technology jobs, effective communication is the bridge that links disparate groups and stakeholders. Here, TPMs beam as experienced translators, deciphering the complex language of tech for non-technical stakeholders. They link the gap, making sure that everyone, no matter their technical history, comprehends the project's objectives and development.
They have the foresight to recognize potential challenges, varying from unforeseen technological difficulties to external variables past the group's control. Threat management isn't concerning removing uncertaintiesit's concerning encountering them head-on. TPMs develop methods to mitigate risks, guaranteeing that the job cruises with thundercloud with strength. They are the guardians of job security, constantly checking the perspective for possible disturbances and all set to release countermeasures when needed.
Right here, TPMs take on the function of allocators-in-chief, tactically dispersing resources to enhance effectiveness. As the job landscape shifts, TPMs reallocate sources dynamically, ensuring that the team continues to be active and responsive.
Who offers the best Senior Technical Program Manager certification?
TPMs, in this respect, end up being the gatekeepers of excellence. They set stringent standards for every component of the job, from code to style, ensuring that the end item satisfies or surpasses the defined requirements.
TPMs produce a culture where quality is not simply a goal however a practice, penetrating every facet of the job. With their thorough oversight, they infuse confidence in stakeholders and add to the long-lasting success and online reputation of the organization. Being an effective TPM requires even more than just a knack for task monitoring.
What interview questions should I expect as a Technical Program Management Career Path?
While TPMs may not be coding wizards, they require a solid understanding of the technical landscape. This includes experience with the innovations included, an understanding of market trends, and the capacity to understand the ramifications of technical decisions.
TPMs are the interaction nexus of a job. Whether it's sharing complex technological details to a non-technical audience or promoting partnership amongst group participants, reliable interaction is non-negotiable.
As innovation evolves, so does the function of the TPM. Agile has come to be much more than simply a buzzword; it's a method of life for several TPMs.
The assimilation of advancement and procedures, called DevOps, has become a foundation in the TPM's toolkit. This method highlights constant assimilation, constant shipment, and partnership in between growth and operations teams. In the age of large information, TPMs are progressively counting on data-driven insights to inform their decision-making processes. Analytics and metrics play an important function in evaluating project performance and making enlightened adjustments.
How can I prepare for a To Become A Tpm interview?
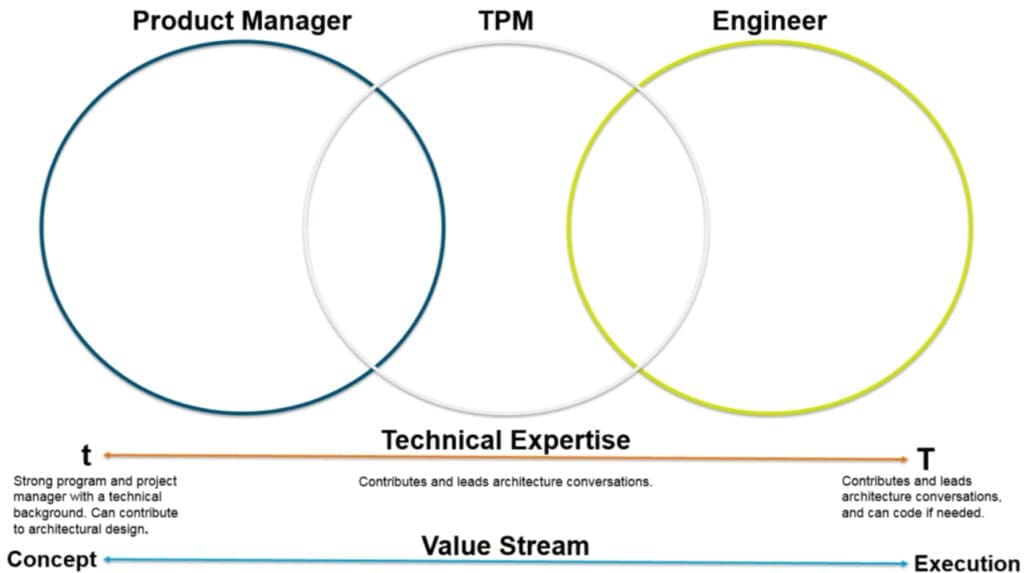
Unlike traditional task supervisors, TPMs need to deeply understand the technological aspects of the jobs they manage. This double expertise permits them to communicate with design groups successfully, recognize technological challenges, and ensure that tasks are finished in a timely manner and within spending plan. Whether you're wanting to work with a TPM or turn into one, recognizing the responsibilities and ability needed is vital for success in the tech market.
The programs cover vital subjects such as project lifecycle monitoring, risk assessment, resource allowance, and software growth processes. With a concentrate on real-world applications, our training ensures you are prepared to take care of the complexities of technological tasks in any type of market. Making an accreditation can substantially enhance your occupation prospects, showing to companies that you have the understanding and skills required to prosper in a TPM duty.
From startups to Ton of money 500 firms, organizations across the globe are looking for qualified specialists to lead their technological programs. Whether you're wanting to work with a TPM or have an interest in TPM jobs, TPM Institute can help you navigate the work market and attach you with the best possibilities. Our courses are not just about discovering; they have to do with launching your job in one of the most desired areas in the technology industry.
Our are dedicated to supplying you with the best possible education and learning, supplying insights based in real-world experience. They are dedicated to helping you attain your qualification and be successful in your job. For additional information concerning our programs and qualifications, at Take the next action in your occupation with TPM Institute and come to be a leader in technological program monitoring.
How do I get started as a Tpm Interview Questions?
There's a propensity for individuals to be attracted toward extremes when conceiving technical program supervisors. The fact is there is a spectrum of technological deepness among TPMs, and this oftentimes differs by job and customer.
They can express complicated technological concepts to non-technical stakeholders and promote partnership between diverse teams. TPMs succeed at determining and dealing with problems that arise during task execution, making sure that tasks remain on schedule and within budget.
TPMs work to ensure that all employee are functioning in the direction of the exact same objectives, stopping miscommunication and thrown away initiative. They anticipate and adapt to adjustments in task requirements, ensuring that tasks can pivot smoothly when required. TPMs proactively deal with prospective issues, decreasing the chance of project delays and failings. They encourage their groups to explore new ideas and modern technologies, driving continuous renovation and development.
TPMs work to make sure that all team members are functioning in the direction of the very same goals, avoiding miscommunication and wasted initiative. TPMs proactively deal with potential issues, decreasing the chance of project delays and failings.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
How To Prepare For A Software Developer Interview – Key Strategies
System Design Interviews – How To Approach & Solve Them
10 Behavioral Interview Questions Every Software Engineer Should Prepare For
More
Latest Posts
How To Prepare For A Software Developer Interview – Key Strategies
System Design Interviews – How To Approach & Solve Them
10 Behavioral Interview Questions Every Software Engineer Should Prepare For